Explain Why Genes Cause Proteins to Have Different Functions
2 common types of exceptions. Learn faster with spaced repetition.
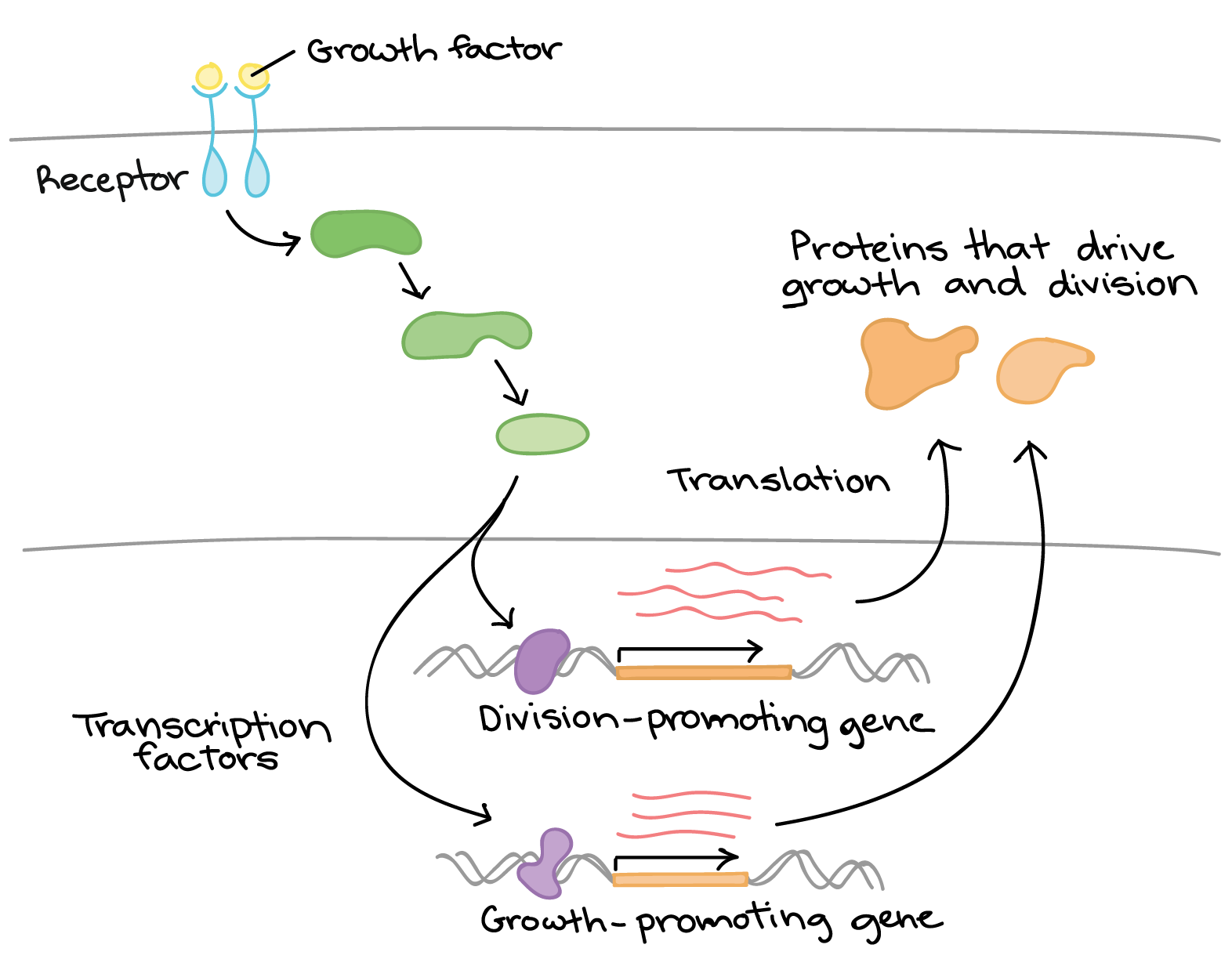
Overview Eukaryotic Gene Regulation Article Khan Academy
Genetics provides a powerful solution to this problem because mutants that lack a particular gene may quickly reveal the function of the protein that it encodes.
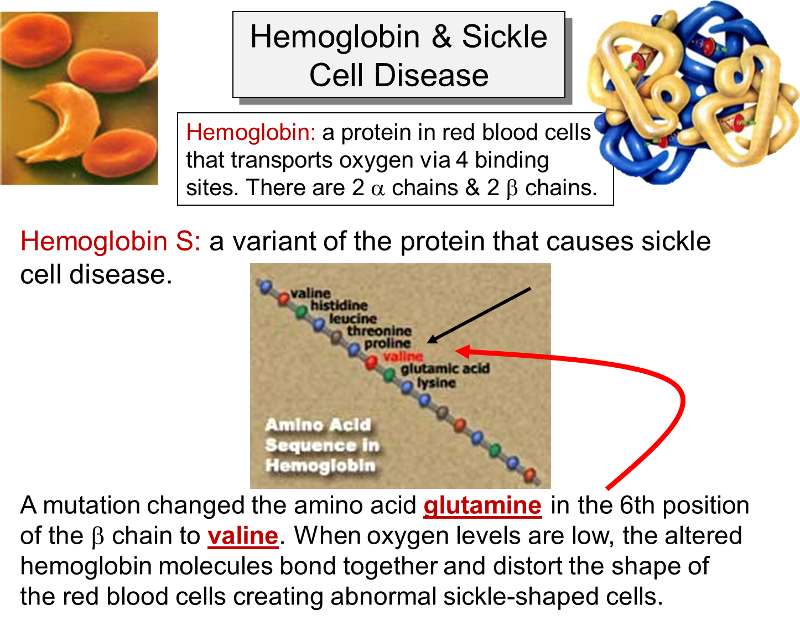
. BTW a common question on Quora is what is a good student project in computational biology and this could be a. In sickle cell anemia the hemoglobin β chain has a single amino acid substitution causing a change in protein structure and function. As a result the protein made from the gene may not function properly.
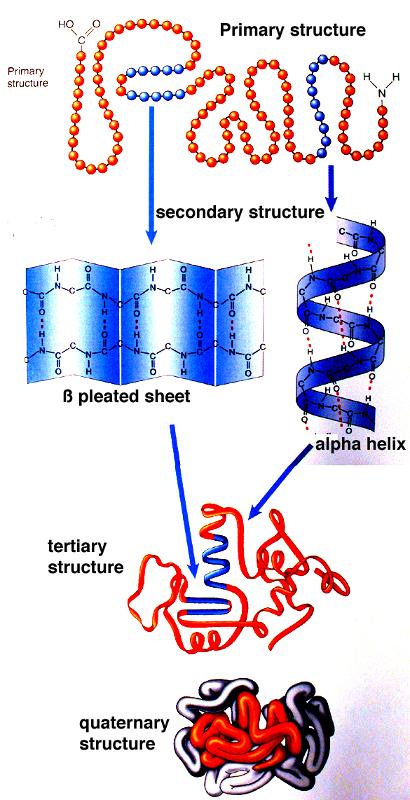
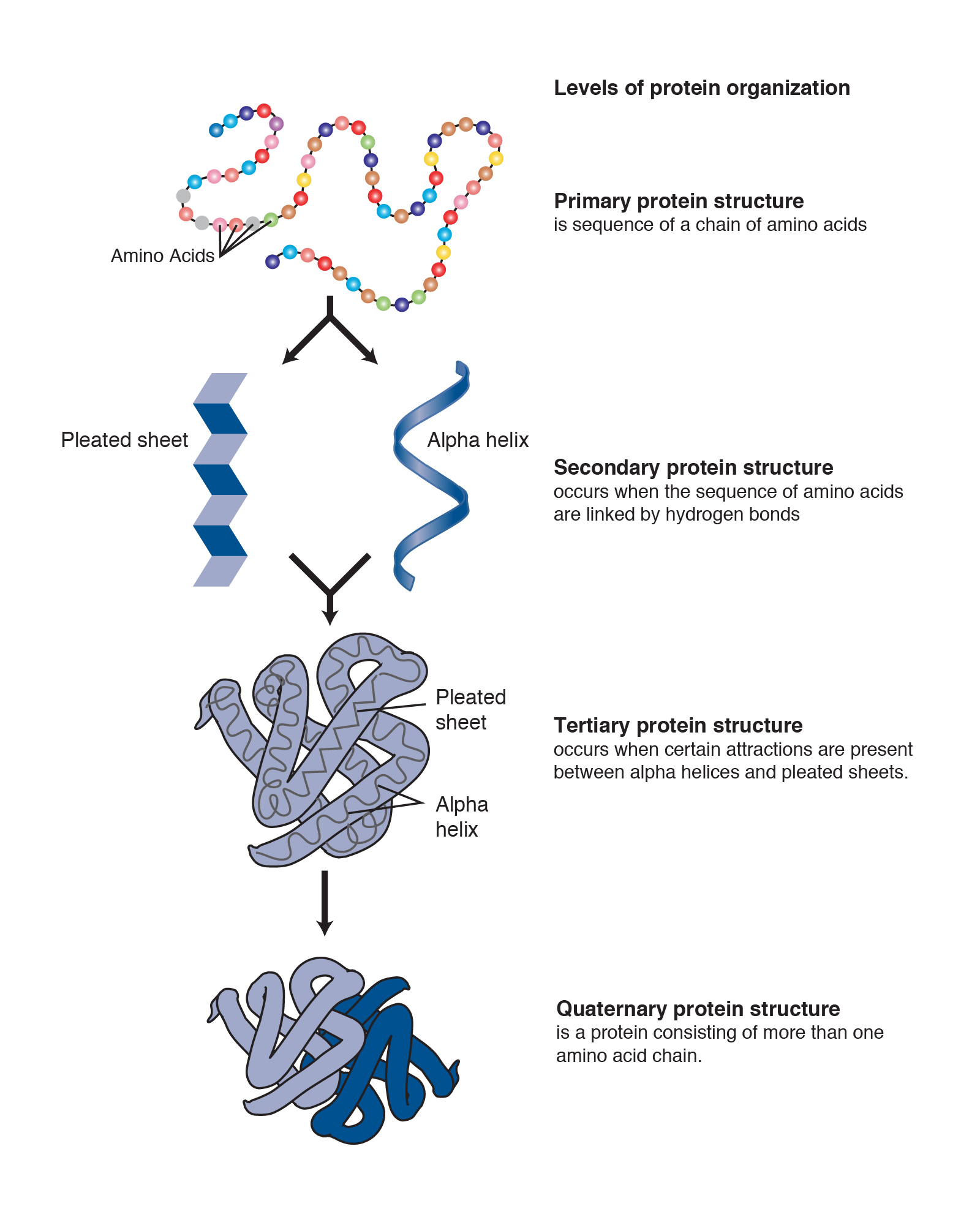
Proteins can be described according to their large range of functions in the body listed in alphabetical order. Each type of protein has a unique three-dimensional shape determined by how the protein folds up. Study 14 - genetic control of protein structure and function flashcards from Emily Godbolds uctc class online or in Brainscapes iPhone or Android app.
When a mutation occurs in a proto. In some cases the duplication leads to the gain of a new function but in. These different patterns of gene expression cause your various cell types to have different sets of proteins making each cell type uniquely specialized to do its job.
One of these genes codes for a protein that prevents cell division. So one gene for two proteins see figure below. Why Do All Cells Have The Same Dna But Different Functions.
Thanks to gene regulation each cell type in your body has a different set of active genesdespite the fact that almost all the cells of your body contain the exact same DNA. Cells have to fulfill multiple different functions to be able to build complex multicellular organisms. Gene expression is often interpreted in terms of protein levels both for peptide hormones and receptors but in my experience when both are measured the correlations are not very strong.
Many cells have common requirements but they wont necessarily have solved them with proteins that share a common evolutionary origin. The gain-of-function of the Ras gene produces excessive growth-promoting signals which increases the cell division leading to cancer development. Which genes of the DNA are turned on determine the functions and kinds of cell.
One copy is not enough. Click to see full answer. The sequence of amino acids determines each proteins unique 3-dimensional structure and its specific function.
A gene that causes a cell to become cancerous is called an _____ oncogene. The substances formed from bile steroids by Clostridium bacteria may cause gene mutation. A deletion changes the DNA sequence by removing at least one nucleotide in a gene.
Genes are a section of DNA that are in charge of different functions like making proteins. Proteins are complex molecules. Long strands of DNA with lots of genes make up chromosomes.
An_____ is a gene that encodes proteins that inhibit cell division. A mutation in DNA alters the mRNA which in turn can alter the amino acid chain. Ras gene is a proto-oncogene which encodes an intracellular signal-transduction protein.
Small deletions remove one or a few nucleotides within a gene while larger deletions can remove an entire gene or several neighboring genes. Amino acids are coded by combinations of three DNA building blocks nucleotides determined by the sequence of genes. This leads to different proteins one in which all 3 exons are used and one in which only exon 1 and 3 are used.
Genes are responsible for all aspects of life. The hundreds of different protein kinases in a eucaryotic cell are organized into complex networks of signaling pathways that help to coordinate the cells activities drive the cell cycle and relay signals into the cell from the cells environment. For example melanocytes in the skin are highly specialized cells which mostly make the pigment melanin.
Many of the extracellular. Although all calls have the DNA only some parts of it are turned on different cells this is called gene expression. Gene duplication happens when an extra copy of a gene is made in an organisms genome.
Such proteins normally help prevent cells from becoming cancerous. If it does not fold up into the correct shape it cannot carry out. Proto-oncogenes are a class of genes that produce proteins to enhance cell division and prevent cell death.
Answer 1 of 3. A change in the nucleotide sequence of the genes coding region may lead to adding a different amino acid to the growing polypeptide chain causing a change in protein structure and function. Gene regulation is how a cell controls which genes out of the many genes in its genome are turned on expressed.
Healthy proto-oncogenes make proteins that help with cell function. The only difference is that instead of just splicing the introns out some exons might be spliced out too. Loss-of-function mutations are usually recessive since in most cases a single good copy of the gene will suffice.
We have seen that searching for homologous genes and analyzing gene expression patterns can provide clues about gene function but they do not reveal what exactly a gene does inside a cell. A proto-oncogene cant cause cancer unless a mutation occurs turning it into an oncogene. Differently expressed genes lead to different proteins made in the cell which leads to different morphology shape or function.
Loss-of-function usually means that less of a protein is made or that some function of the protein has been compromised. Thanks to gene regulation each cell type in your body has a different set of active genesdespite the fact that almost all the cells of your body contain the exact same DNA. The Regulation of Cdk and Src Protein Kinases Shows How a Protein Can Function as a Microchip.
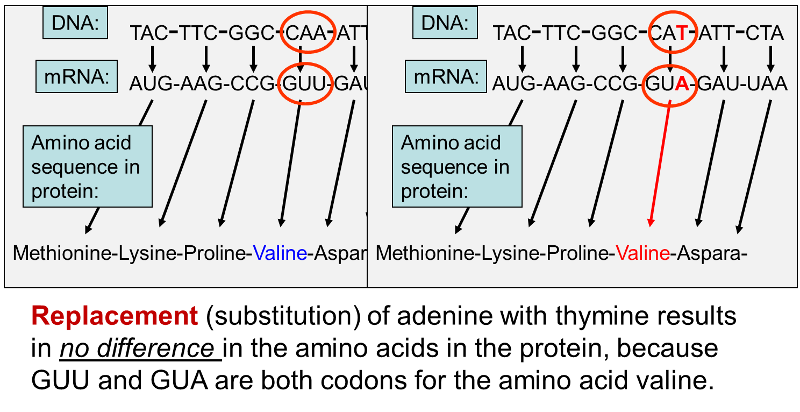
A base substitution may have three different effects on an organisms protein. And a base substitution can also cause a silent mutation in which the proteins function doesnt change at all. Human cells contain genes that control their growth and division.
The example discussed here concerns a gene with only 3 exons.

Genes And Chromosomes 3 Genes Proteins And Mutations Nursing Times

Intro To Gene Expression Central Dogma Article Khan Academy

The Phosphorylation Of A Protein Can Make It Active Or Inactive Learn Science At Scitable

Dna Can T Explain All Inherited Biological Traits Research Shows Dna Biology Chromosome

Genes And Chromosomes 3 Genes Proteins And Mutations Nursing Times
Proteins Perform Many Functions

Proteins Perform Many Functions
Proteins Perform Many Functions
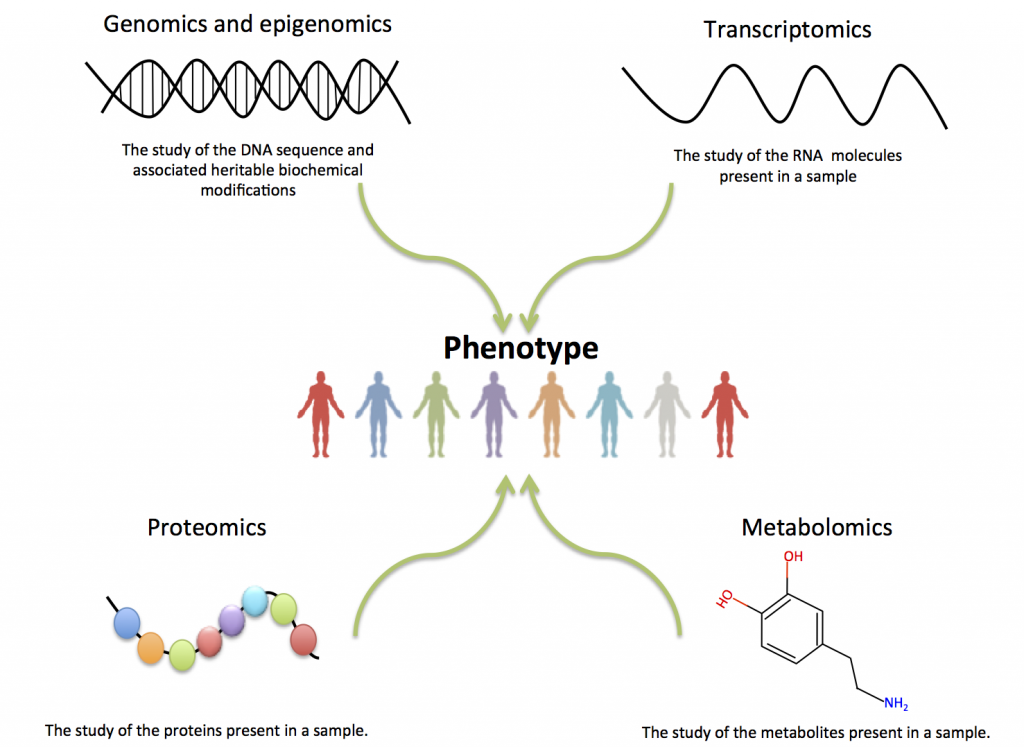
What Is Functional Genomics Functional Genomics I
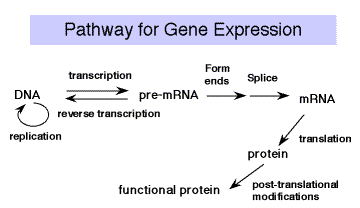
Part Three Gene Expression And Protein Synthesis
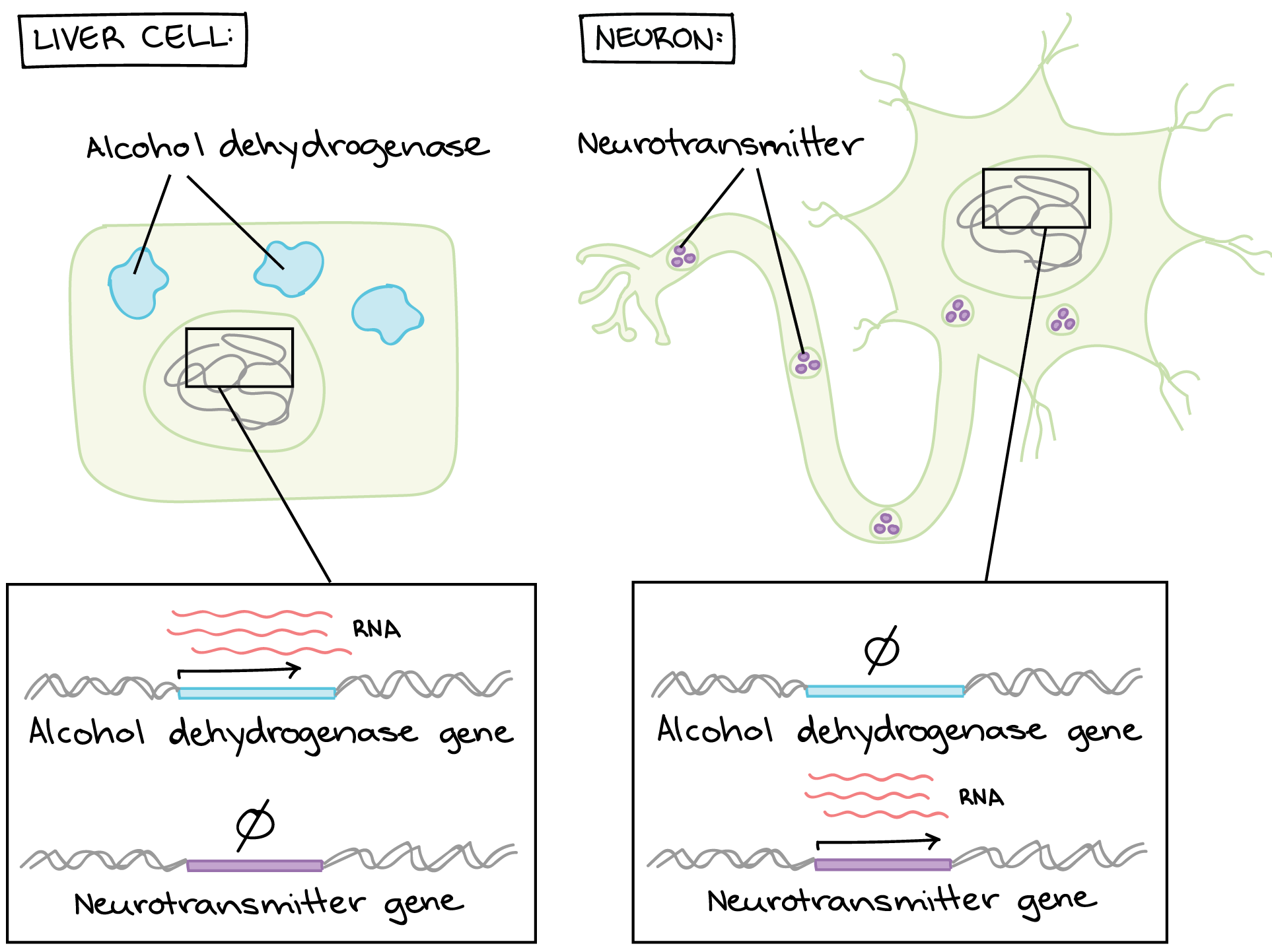
Overview Eukaryotic Gene Regulation Article Khan Academy

Genes And Chromosomes 3 Genes Proteins And Mutations Nursing Times

Getting Started With Genetics Genetic Lifehacks Genetics Activities Dna Genetics Dna Activities

Functions Of Proteins 5 Main Functions What Where How
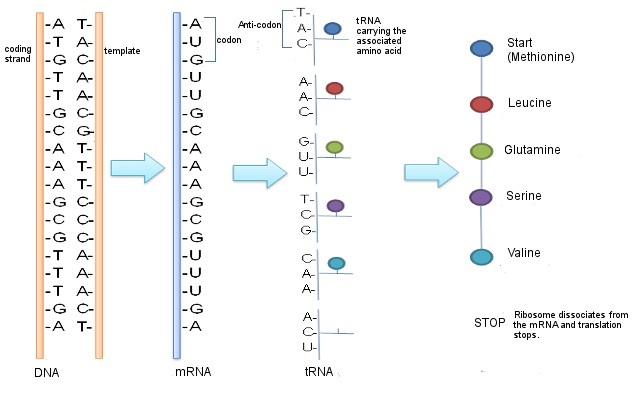
How Do Genes Direct The Production Of Proteins Mt Hood Community College Biology 102

Genetic Mutations Can Change How Proteins And Cells Function This Infographic Outlines How Proteins Are Ma Cancer Genetics Molecular Genetics Biology Activity

Gene Expression Regulates Cell Differentiation Learn Science At Scitable

Comments
Post a Comment